Abstract
Introduction
The international prognostic index for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL; CLL-IPI) combines patient and disease characteristics to predict disease outcome. Among the included variables, IGHV unmutated status is associated with an inferior prognosis. In Denmark, according to national guidelines, most CLL patients requiring treatment are offered Rituximab in combination with either Cyclophosphamide and Fludarabine (FCR) or Bendamustine (R-Benda), or CD20 targeted antibodies combined with chlorambucil (CD20-chl), except patients with del(17p)/p53 mutation-positive CLL, for whom targeted treatment has been shown to be superior. The choice between FCR, R-Brenda and CD20-chl is made in consensus with the patient and depends on age, kidney function, and comorbidities. Interestingly, it is not known if FCR, R-Benda and CD20-chl impact overall survival (OS) differently for respectively IGHV unmutated and mutated CLL outside clinical trials, i.e. in a truly population-based setting.
Method
All patients diagnosed with CLL in Denmark since 2008 are registered in the Danish CLL database, which includes information on gender, birthday, date of diagnosis, IGHV mutational status and other prognostic variables, date of treatment and treatment regimen. Using this information, we assessed OS from treatment initiation for patients with known IGHV-status with follow up until November 2016 by means of Kaplan-Meier and Cox analyses.
Results
In total 2916 patients had a known IGHV mutational status, 60% were male, median age at diagnosis was 70 years, and 933 (32%) patients had IGHV unmutated CLL. OS was significantly shorter for IGHV unmutated CLL than for mutated CLL from time of diagnosis (p<0.0001). Overall, 939 patients were treated for CLL during follow up and thus included in the analysis. The treatment consisted of FCR for 291 patients (31%), R-Benda for 97 (10%), Chlorambucil for 304 (32%), single agent Rituximab for 59 (6%) and other drugs for 188 (20%). Among the patients treated with Chlorambucil 89 also received CD20 antibodies.
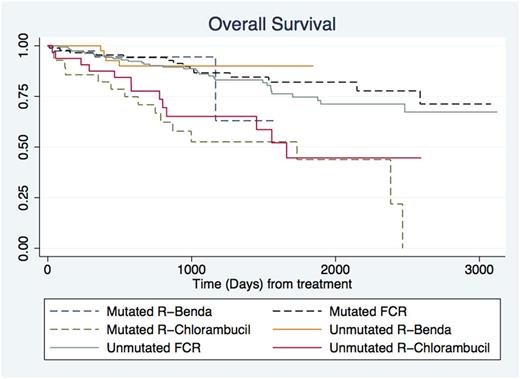
OS from start of treatment was analyzed for three treatment groups, median age in the groups varied; FCR 61 years, R-Benda 67 years, Chlorambucil 78 years, Rituximab 73 years and other drugs 69 years. The number at risk in the treatment groups was: Mutated R-benda 39, Unmutated R-benda 43, Mutated FCR 88, unmutated FCR 159, Mutated R-Chlor 28 and Unmutated R-Chlor 32. The 3-year OS from treatment initiation was: Mutated R-benda 95%, Unmutated R-benda 90%, Mutated FCR 88%, unmutated FCR 89%, Mutated R-Chlor 52% and Unmutated R-Chlor 65%. No differences were observed in OS from time of treatment between FCR and R-Benda treated patients, neither overall nor among patients with mutated nor unmutated IGHV CLL. Meanwhile, patients treated with CD20-chl had a significantly lower OS regardless of IGHV mutational status compared to other treatment groups (See Figure).
Discussion and conclusions
Consistent with current evidence and clinical trial results, patients with unmutated IGHV CLL had a significantly worse prognosis compared to patients with mutated IGHV CLL from time of diagnosis. Despite patients treated with R-Benda being slightly older than patients treated with FCR, OS from time of treatment was similar and no difference was seen between IGHV mutated and unmutated patients. This is in accordance with findings from the CLL10 study [Eichhorst et al, LancetOnc 2016], however unexpectedly the increased median age for R-Benda treated patients does not lead to a worse OS. For patients treated with CD20-chl, OS was significantly worse. This likely reflects guidelines recommending chlorambucil-based regimens for patients with significant comorbidity.
Most importantly for treating physicians and their patients, an excellent outcome with chemoimmunotherapy for patients with CLL in clinical practice is demonstrated with a 3-year OS from start of treatment of 88-95% for R-Benda and FCR treated patients and 52-65% for CD20-chl treated patients. Thus, chemoimmunotherapy still have a role to play for treatment of patients with CLL. Detailed analyses of second line treatment with data on del(17p)/TP53 mutation and longer follow up also for patients treated with targeted treatment are underway. Shared clinical decision making for patients with CLL could be further informed by these real world evidence based outcomes.
Andersen: AbbVie: Other: Travel grant. Niemann: Roche: Consultancy, Other: Travel grant; Novo Nordisk Foundation: Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel grant, Research Funding; Gilead: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel grant; Janssen: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel grant; The Danish Cancer Society: Research Funding; Novartis: Other: Travel grant. Frederiksen: Gilead: Research Funding; AbbVie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal